Learn About the Lab Philosophy
If you would like to know more about the general philosophy of the lab, please listen to this Freakonomics podcast interview with Jack Gallant or to these OHBM discussions between Peter Bandettini and Jack Gallant (discussion 1, discussion 2).
Learn About Voxelwise Encoding Models
Voxelwise Encoding Model review paper
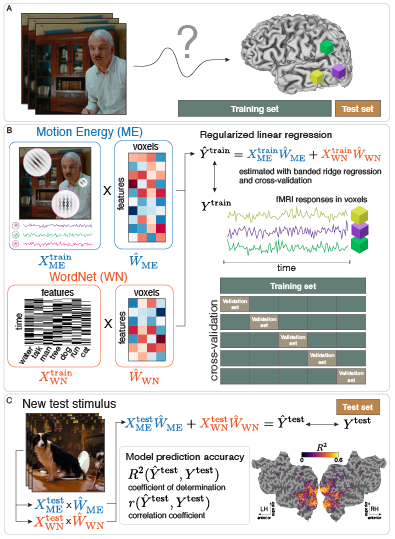
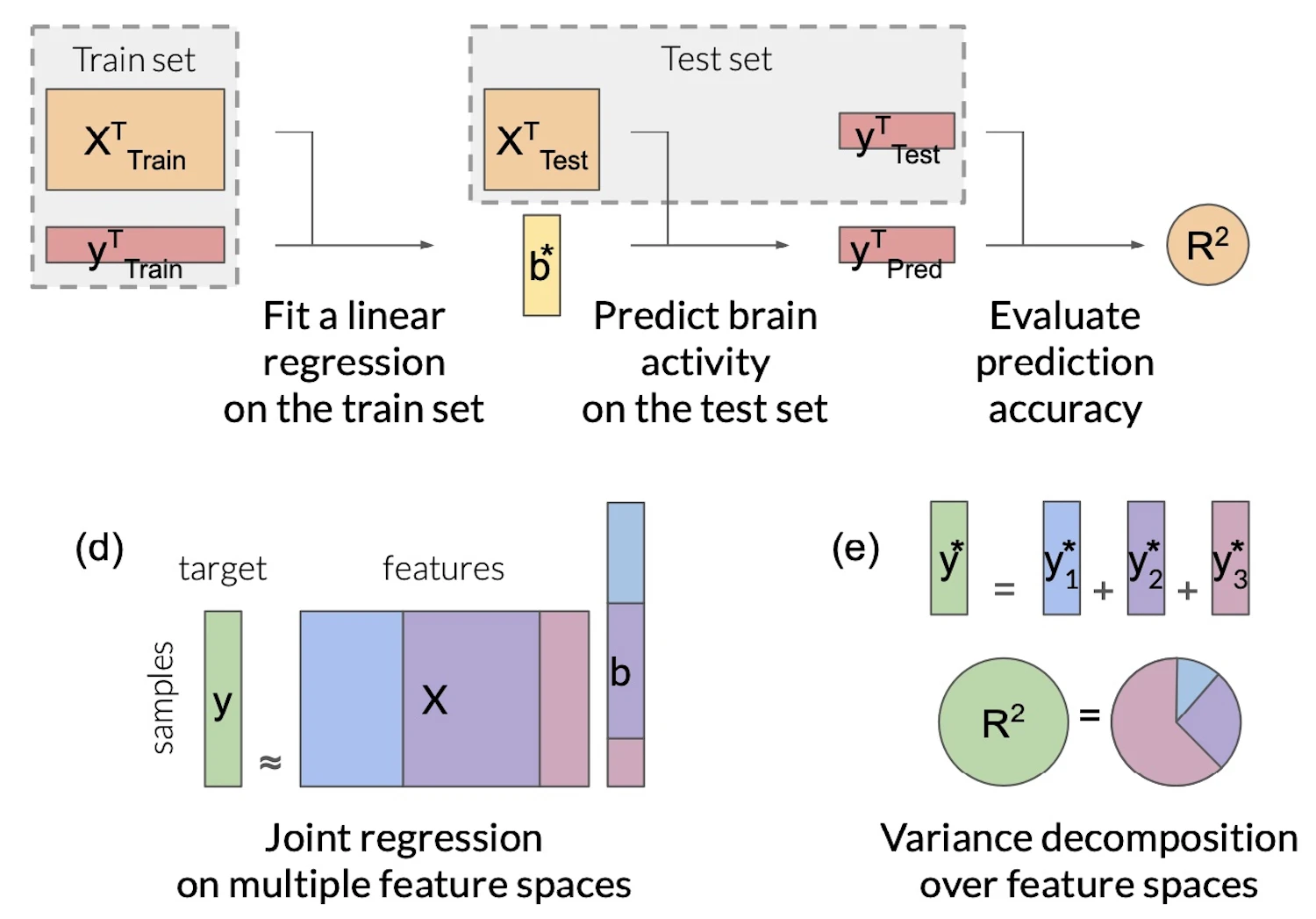
This review paper provides the first comprehensive guide to the Voxelwise Encoding Model (VEM) framework. The VEM framework is a framework for fitting encoding models to fMRI data. This framework is currently the most sensitive and powerful approach available for modeling fMRI data. It can be used to fit dozens of distinct models simultaneously, each model having up to several thousand distinct features. The Voxelwise Encoding Model framework also conforms to all best practices in data science, which maximizes sensitivity, reliability and generalizability of the resulting models.
Voxelwise Encoding Model tutorials
These Python tutorials show how to fit, evaluate, and interpret voxelwise encoding models on one of our public available datasets. We are providing these online tutorials here as a service to the fMRI community.
Voxelwise Encoding Model workshop video
At the 2021 CCN meeting we held a keynote and tutorials session on the Voxelwise Encoding Model framework. You can find a video recording of the workshop here.
Theory paper focusing on feature space selection and banded ridge regression.
December 1, 2022
Encoding models identify the information represented in brain recordings, but fitting multiple models simultaneously presents several challenges. This paper (Dupré la Tour et al., Neuroimage, 2022) describes how banded ridge regression can be used to solve these problems. Furthermore, several methods are proposed to address the computational challenge of fitting banded ridge regressions on large numbers of voxels and feature spaces. All implementations are released in an open-source Python package called Himalaya.
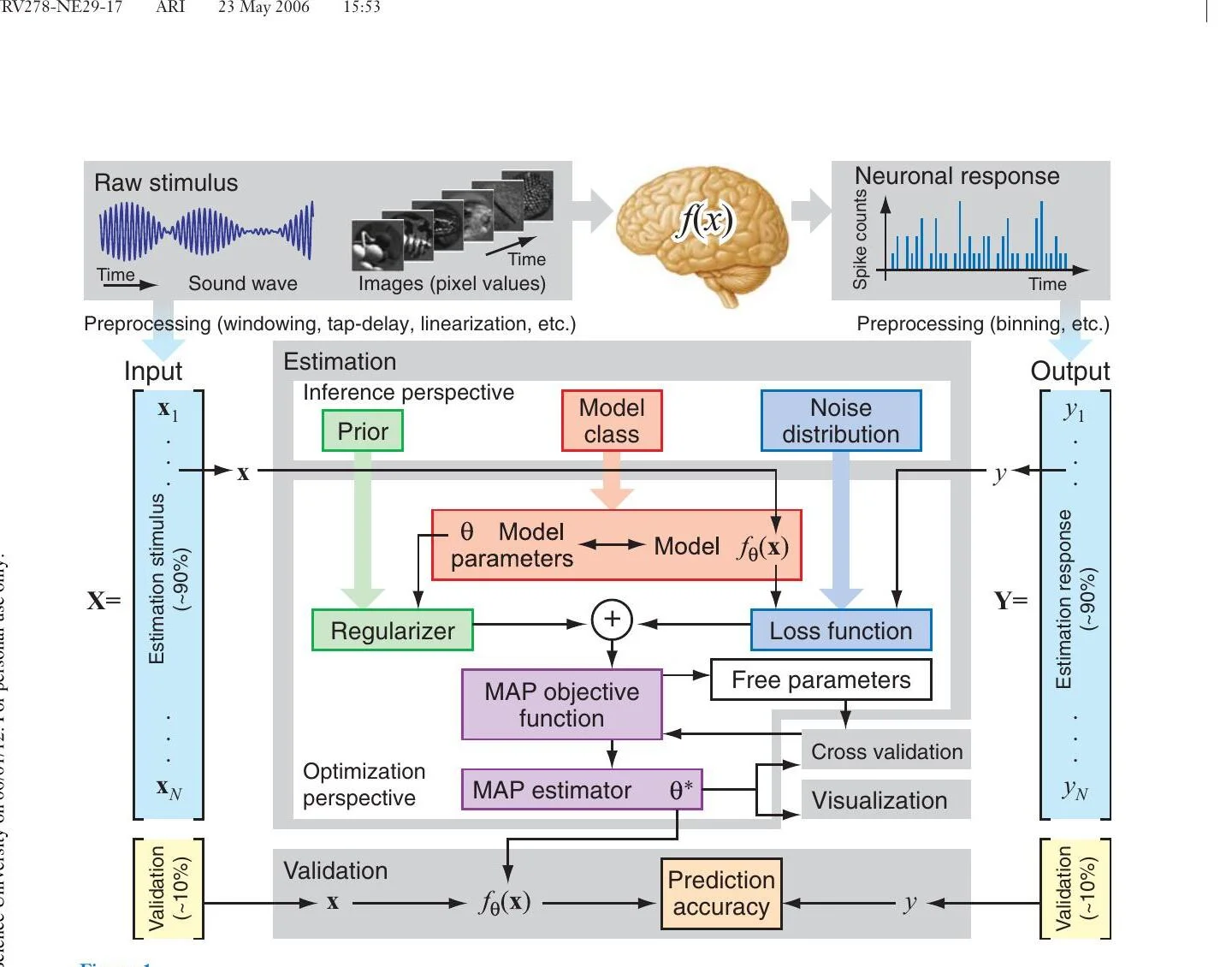
System identification review for sensory neuroscience
This review paper (Wu, David & Gallant, Annual Review of Neuroscience, 2006) provides a comprehensive introduction to system identification methods for sensory neuroscience. The paper shows how many different algorithms used in sensory neurophysiology can be viewed as variants of a single statistical inference problem: maximum a posteriori (MAP) estimation. It covers practical issues including stimulus selection, model estimation, regularization, visualization, and prediction-based validation. This paper provides the theoretical foundation for the encoding model framework used in the Gallant Lab.